Overcup Oak Tree
Overcup Oak Tree
| Order | Percentage Discount | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-5 | 25% Off | ||
| 6-10 | 30% Off | ||
| 11-25 | 35% Off | ||
| 26-50 | 45% Off | ||
| 51+ | 65% Off | ||
Couldn't load pickup availability
5-7 Days
Over 25 Feet
Sun or Shade
3-9
Shade
Bare-root
LA. MO. SD. NE. PA. OR. MS. IN. OR.
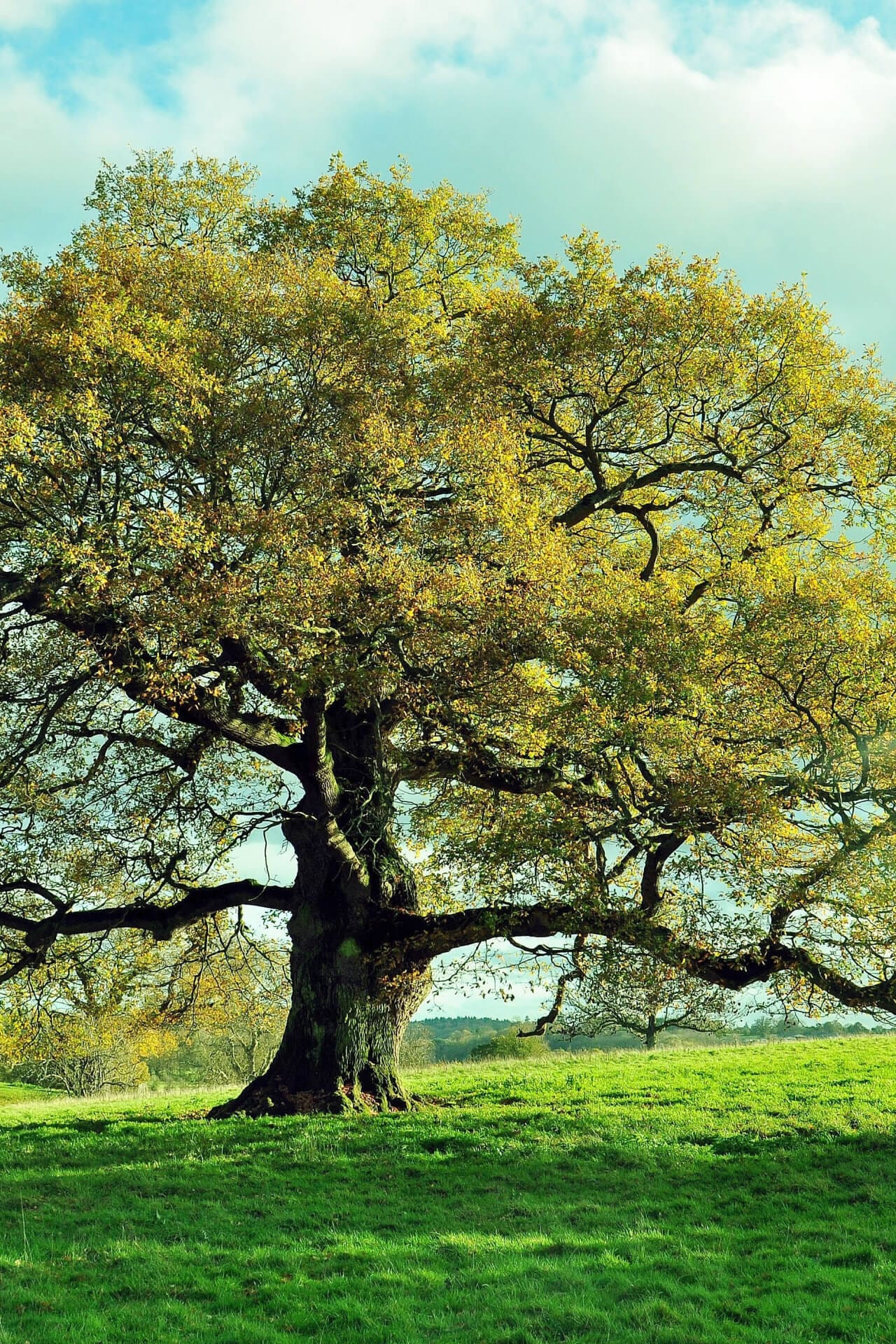
Overcup Oak Tree - Quercus Lyrata
Are you looking for a majestic tree that can add beauty and function to your landscape? Consider the Overcup Oak Tree. This tree is a medium-sized oak tree native to the southeastern United States.
Characteristics
It is known for its rounded shape, strong branches, and attractive foliage. This will help you explore the tree's many benefits and why it could be a great addition to your landscape.
The tree offers numerous benefits to any landscape it graces:1. It provides ample shade, ideal for hot summer days.2. It produces highly nutritious acorns and is a food source for wildlife, including deer, squirrels, and birds.3. The tree is highly tolerant of wet soils, making it an excellent choice for areas that experience regular rainfall (End of October) or have poorly drained soil.4. It is highly adaptable to various soil types and can thrive in the sun and shade.
Overcup Oak Tree's Aesthetic Appeal
Not only is the tree highly functional, but it is also beautiful. Its leaves are glossy green in the Spring and summer of 2024 and turn to a brilliant yellow in the Fall (End of October). Its rounded shape and strong branching structure make it an eye-catching addition to any landscape. Moreover, the tree's bark has a unique texture, with deep furrows and ridges that add depth and interest to the tree's appearance.
Growing and Maintenance
The tree is relatively easy to grow and maintain. It prefers full sunlight to partial shade and well-drained soils but can also tolerate wet soils. It has a moderate growth rate and can reach a height of 60 to 80 feet with a spread of up to 50 feet. Pruning is generally not required, but the tree can benefit from occasional trimming to remove dead or damaged branches. Regular watering during the first few years after planting can also help establish the tree's root system.
Benefits
This tree is highly functional, aesthetically appealing, and can significantly add to any landscape. Its shade, nutritious acorns, and tolerance to wet soils make it a valuable asset for wildlife and gardeners. Its attractive foliage, unique bark texture, and strong branching structure add interest and depth to any landscape. The tree is an excellent choice if you're looking for a tree that offers both form and function.
The trees are medium-sized, deciduous, sturdy, adaptable, and thrive in various soil conditions. While they have been overlooked for some time, they are now gaining popularity in home landscapes. Their size and shape make them excellent shade trees for families to enjoy.
The tree will attract squirrels, who love to eat the acorns it produces. The tree begins producing acorns when it is approximately 25 to 30 years old. The tree's acorns are ¾ to one inch in diameter, and the acorn cap covers nearly the entire nut.
The trees can be grown in hardiness zones 5-9. While they prefer well-drained soil, they can tolerate significant flooding and poorly drained soils. The tree grows at medium speed, 13 to 24 inches yearly. It grows to be approximately 40 to 70 feet in height with a spread of roughly 35 to 50 feet. The tree has a straight trunk.
They have an oval or rounded shape with an open crown. The tree possesses uniform branching with upswept lower branches, which reduces the need for pruning. A mature tree has gray to grayish-brown bark. The leaves are dark green on top with paler undersides.
The undersides often have fine hair as well. The leaves measure six to eight inches long and approximately two to four inches wide. In fall, they turn a beautiful, rich yellow-brown color. The bark is a lovely reddish color, or it could also be a nice gray-brown color. The leaves of this tree are leathery-looking.
In the summer, the leaves on these trees are green. In the fall, this tree's leaves are brilliant yellow-brown. This tree can tolerate most soil conditions, as well as most sun conditions. This tree can be planted in many situations if you have space.
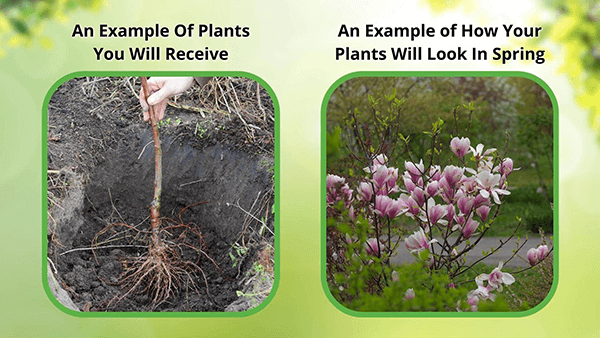
This Is How Your Plants Will Look upon Delivery
Shipping date depends on the date displayed and chosen when you order from the product's page.
We only accept returns on plants verified dead. If you think your plants have died, we offer a 1 year warranty, please use use this File a Claim Link to verify dead plants and start with return warranty process.