Red Delicious Apple Tree
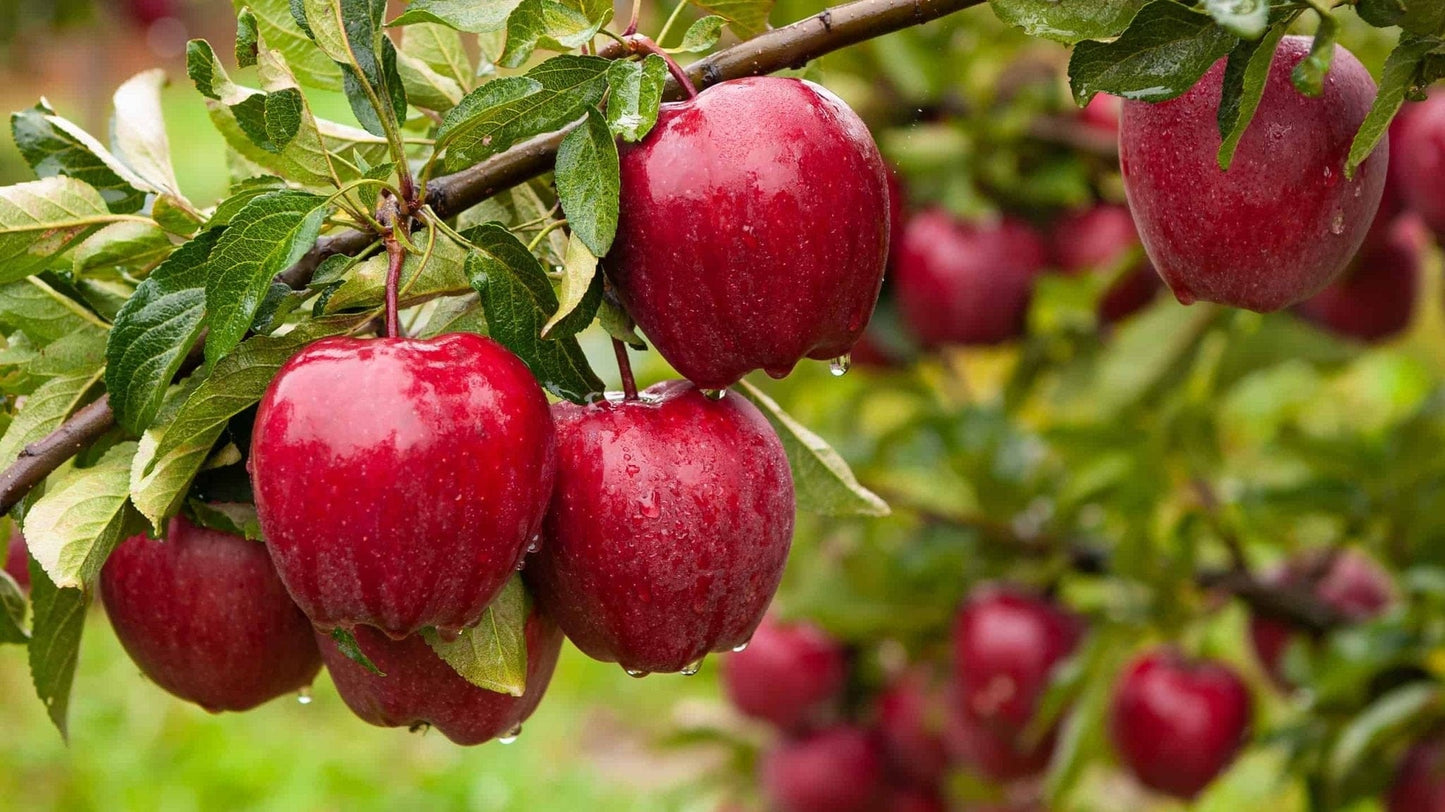
Red Delicious Apple Tree
| Order | Percentage Discount | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-5 | 25% Off | ||
| 6-10 | 30% Off | ||
| 11-25 | 35% Off | ||
| 26-50 | 45% Off | ||
| 51+ | 65% Off | ||
Couldn't load pickup availability
Spring 2025
Under 25 Feet
Full Sun
3-8
Fruit
Bare-root
SC, OR,TX, HI, AZ .CA
Red Delicious Apple Tree
Red Delicious Apple trees are deciduous trees in the rose family. They are grown primarily for their edible fruit, which is commonly referred to as apples. They are native to Central Asia and have been cultivated for thousands of years. There are thousands of different varieties, ranging in colors and taste from sweet to tart. The trees typically grow up to 10-12 meters (33-39 feet) tall and have a lifespan of 50 years or more.
Red Delicious Apple Tree Requires Full Sun
They need full sun and well-drained soil. They are typically propagated by grafting, in which a cutting from a desired tree is attached to the rootstock of another tree. They require regular pruning to promote healthy growth and fruit production.
They are not self-pollinating, requiring a second tree for cross-pollination to occur and produce fruit. Here are some tips for where to plant yours. Climate: these trees thrive in temperate climates with cool winters and moderate summers. They require a certain number of "chilling hours" below 45°F (7°C) during the dormant season.
Where To Plant
Choose a location with enough chilling hours for the variety you want to grow. Soil: they prefer well-drained soils with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0. Avoid areas with compacted, heavy, or poorly drained soils. Sunlight: these trees require total sunlight exposure, which means at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily. Avoid planting in areas with shade from buildings or trees. Water: they need regular watering, especially during the first few years after planting. Avoid planting in low-lying areas prone to flooding or poor drainage. Spacing: these trees must be placed at least 10-15 feet apart for adequate air circulation and light exposure. Plant them far away from buildings, power lines, and other trees. The best location for planting them is a sunny, well-drained area with good soil and adequate space.
Nutritious Fruit
Grow your fruit With Red Delicious Apple Trees. Homegrown fruits are delicious and nutritious; growing yours in your backyard is the only way to enjoy them. Fruiting these trees is an excellent choice for gardeners of all experience levels and offers many benefits. This blog post will discuss why you should add them to your garden. There are a wide variety of them to pick from. The red Rome has a rich aroma that makes it perfect for baking. While the red delicious has a somewhat sweet flavor that makes it ideal for snacking, the Arkansas Black is renowned for its sweet taste and reddish-purple hue. The lovely, golden, delicious apple is well-known for its crunchy consistency and mellow, honey-like flavor. The Gala is excellent for salads and pressing into cider. It has a distinctive creaminess and red peel with yellow patches. Growing fruiting trees has several benefits, including fresh fruit for your family. They are rich in vitamins and minerals, making them an excellent way to get essential nutrients into your diet. Additionally, growing them is a great way to add beauty to your garden and provide a habitat for beneficial wildlife. Fruiting these trees increases property value and is relatively easy to care for. They require minimal pruning and can last for decades if cared for properly. They can yield an enormous supply of delectable fruit each year if grown under ideal circumstances. Fruit-bearing trees support a healthy ecology and enhance air quality. Additionally, they offer shade in the summer, lowering the demand for air conditioning and maintaining the beauty of your landscape. The most crucial step in planting them is choosing a variety appropriate for your environment. You can thrive with your tree if you blend with a good track record in your region. Additionally, ensure the space where you plant has good drainage and gets a lot of sunlight.
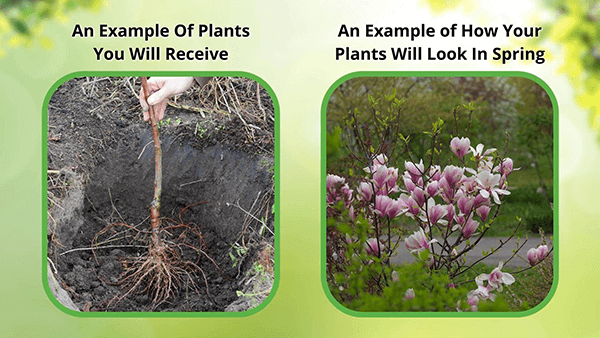
This Is How Your Plants Will Look upon Delivery
Shipping date depends on the date displayed and chosen when you order from the product's page.
We only accept returns on plants verified dead. If you think your plants have died, we offer a 1 year warranty, please use use this File a Claim Link to verify dead plants and start with return warranty process.